The application of industrial CT technology in defect detection of lithium batteries
Release time:2024-06-17Publisher:Jeenoce
Computer tomography technology, abbreviated as CT technology, is mainly applied in the medical field to detect the internal health status of the human body. With the development of related technologies, especially the resolution of radiation sources and detection devices, CT technology is gradually being applied in the field of industrial manufacturing and production.
By conducting a comprehensive scan of the internal structure of the test sample, different contrast fault images are formed based on the density differences of the internal structure, accurately grasping the number, volume fraction, distribution and other information of pores, inclusions, cracks, and the three-dimensional space of the material microstructure inside the sample. This is conducive to analyzing the relationship between material defect information and mechanical properties, identifying the role of defects in material failure, and helping to study the failure mechanism to optimize and improve the preparation process of materials.
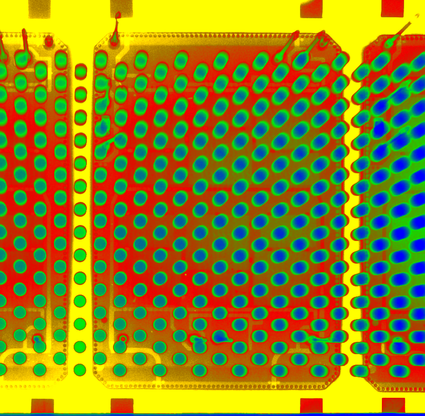
At present, in the defect detection of new energy lithium batteries, industrial CT technology has gradually become one of the most effective detection methods. It can not only observe the internal structure of the battery in a non-destructive state, but also magnify the battery sample by hundreds of times to find subtle defects. In terms of battery aging degree, industrial CT can be used to compare the evolution of the overall internal structure of the battery after different cycle cycles in detail; In terms of battery safety hazards, industrial CT scans are used to analyze the characteristics of electrode breakage, electrode wrinkles, electrode alignment, and internal foreign objects in computer tomography images. The internal structure of the battery after safety testing is analyzed.
Lithium ion batteries are subject to collisions during production, resulting in surface defects such as dents, scratches, bulges, etc., which can be visually detected through industrial CT.
Lithium batteries are mainly composed of positive electrode, negative electrode, isolation film, and electrolyte. The material compaction density of positive and negative electrode plates affects the internal pore distribution, and a uniform pore distribution is conducive to the smooth transmission of electrolyte on the electrode plates. Industrial CT analyzes the compaction density of lithium battery electrodes through three-dimensional characterization.
Industrial CT machines have become an essential testing method in the research and production process of lithium batteries due to their advantages of non-destructive, intuitive, and visual inspection.

