Temperature curve setting for lead tin paste reflow soldering
Release time:2024-04-11Publisher:Jeenoce
Although lead-free products are the trend now, there are also many products that use lead-tin paste for reflow soldering. So, what is the temperature curve setting for reflow soldering with lead-tin paste? JEENOCE will introduce it in detail below:
1、 Temperature curve setting for preheating zone of lead tin paste reflow soldering
The reflow soldering preheating zone, also known as the ramp zone, is used to raise the temperature of the PCB from the surrounding environment temperature to the required active temperature. In this area, the temperature of lead products continues to rise at a rate not exceeding 2-5 ° C per second. If the temperature rises too quickly, it may cause certain defects, while if the temperature rises too slowly, the solder paste will become overly sensitive, and there is not enough time to reach the active temperature of the PCB.
The preheating zone of the reflow soldering furnace generally accounts for 25-33% of the entire heating channel length. If the heating rate is too fast, it may cause the fluidity and deterioration of the composition of the solder paste, resulting in phenomena such as solder balls and bridging. At the same time, it will cause excessive thermal stress on the components and damage them.
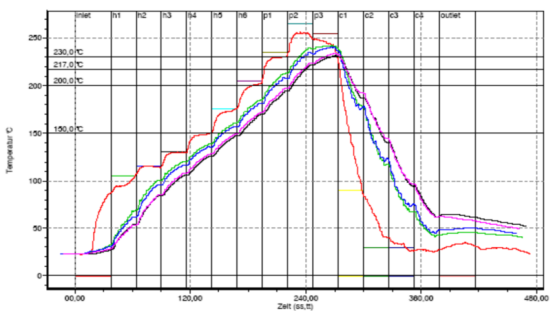
2、 Temperature curve setting for active zone of lead tin paste reflow soldering
The active zone, sometimes referred to as the dry or wet zone, usually occupies 33-50% of the heating channel and has two functions. The purpose is to sense the temperature of the PCB at a relatively stable temperature, allowing components of different qualities to be homogeneous at temperature and reducing their significant temperature difference. The second function is to allow the flux to be activated and volatile substances to evaporate from the solder paste.
The common active temperature range for reflow soldering of lead tin paste products is 120~150 ° C. If the temperature in the active zone is set too high and the flux does not have enough time to activate, the slope of the temperature curve is an upward increasing slope. Although some solder paste manufacturers allow for some temperature increase during the activation period, the ideal curve requires a relatively stable temperature, so that the temperature of the PCB is equal at the beginning and end of the active zone.
3、 Temperature curve setting for reflow zone of lead tin paste reflow soldering
The reflux zone, sometimes referred to as the peak zone or the highest heating zone. The function of this area is to increase the temperature of PCB assembly from the active temperature to the recommended peak temperature. The active temperature is always slightly lower than the melting point temperature of the alloy, and the peak temperature is always above the melting point.
The typical peak temperature range for lead tin paste reflow soldering is 205~230 ° C. Setting the temperature in this area too high can cause the temperature rise slope to exceed 2-5 ° C per second, or reach a reflow peak temperature higher than recommended. This situation may cause excessive curling, delamination, or burning of the PCB, and damage the integrity of the components. The metal particles in the solder paste melt and form the surface of the solder joint under the action of liquid surface tension.
4、 Temperature curve setting for the cooling zone of lead tin paste reflow soldering
After leaving the reflow zone, the substrate enters the cooling zone, and controlling the cooling rate of the solder joints is also very important. The strength of the solder joints will increase with the increase of cooling rate.
The melting point of Sn63/Pb37 with lead tin paste is 183 ° C. The ideal cooling zone curve should be mirrored with the reflux zone curve. The closer to this mirror relationship, the tighter the solid structure of the solder joint, the higher the quality of the obtained solder joint, and the better the bonding integrity.

