X-RAY detection principle and advantages and disadvantages
Release time:2024-07-09Publisher:Jeenoce
The X-RAY testing principle is an important non-destructive testing method in the field of modern technology, widely used in medical, industrial, safety and other fields. Its core lies in using X-rays to penetrate objects and interact with them, detecting and analyzing the X-ray information after penetration, and obtaining key information such as the internal structure and defects of the object.
Firstly, we need to understand the basic characteristics of X-rays. X-rays are high-energy electromagnetic waves with extremely strong penetrating power, capable of penetrating various substances. This characteristic allows X-rays to penetrate deep into the interior of an object and interact with the microscopic structures such as atoms and molecules inside the object. These interactions include phenomena such as absorption and scattering, which are the basis of the X-RAY detection principle. Specialized testing equipment is essential in the X-RAY testing process. These devices typically consist of X-ray generators, detection probes, imaging sensors, etc.
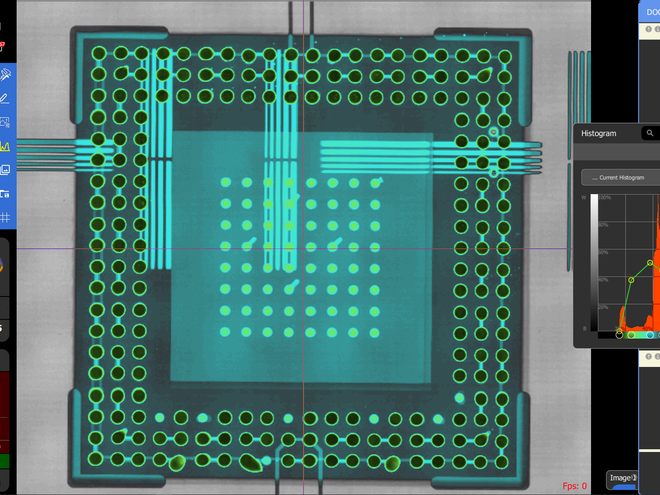
The X-ray generator is responsible for generating high-quality X-ray beams, the detection probe is used to receive X-ray signals after penetrating objects, and the imaging sensor converts the received signals into digital signals for subsequent processing and analysis. When X-rays penetrate an object, each layer inside the object absorbs a certain amount of X-rays. This absorption phenomenon depends on factors such as the thickness, material, and internal structure of the object. By measuring the X-ray intensity after penetrating an object, the structural information inside the object can be inferred. In addition, X-rays can also scatter inside objects, and the scattered X-rays can be captured by detection probes, further revealing the internal details of the object. During the imaging process, the sensor will convert the received X-ray signal into a digital signal and process the image using specific algorithms. These algorithms can be adjusted according to actual needs to better extract and analyze information from images. By observing and comparing the processed images, we can identify potential issues such as foreign objects and defects in the object.
X-RAY detection has multiple advantages.
Firstly, its high sensitivity enables us to detect subtle structures and density changes inside objects. Secondly, as a non-destructive testing method, X-RAY testing does not damage the internal structure of objects, thus ensuring the reliability and safety of the testing. In addition, X-RAY detection can also obtain real-time results, which helps to detect abnormal situations inside objects in a timely manner. However, X-RAY detection also has certain limitations. For example, for certain special materials or structurally complex objects, the penetration ability of X-rays may be limited.
In addition, it should be noted that non-standard use of X-ray related equipment may also cause certain harm to the human body. This is due to the strong penetration of X-rays, which can cause irreversible damage to human tissues. Therefore, special attention should be paid to protecting personnel's safety when using X-ray testing equipment and other fields, such as industrial testing and hospital related chest X-ray CT operations. Scientists have been working hard to improve the X-RAY detection technology in response to these limitations. For example, by optimizing the design of X-ray sources, the quality and penetration ability of X-rays can be improved; Develop more advanced detection probes and imaging sensors to improve the sensitivity and resolution of detection; And research new image processing algorithms to improve image quality and interpretability. In summary, the X-RAY detection principle is a non-destructive testing method based on X-ray penetration and interaction. By utilizing the characteristics of X-rays and specialized detection equipment, we can obtain information on the internal structure and defects of objects, providing strong support for applications in various fields.

